We know you're excited to get set up on your computer. We offer a variety of ways to help you. Ideally, 5 minutes is all you need to get your questions below answered and/or problem fix. For further help and support please feel free to give us a call at 707.412.8314. You can also email us at online@itwebsmith.com. Thank you for choosing IT WebSmith your place where Innovation & Technology comes together.
1How long will it take for my site to appear on Google?
How long does it take for a new site to show up in Google’s search results? How long do I have to wait? How will Google even know to include me? Is there anything I can do to make my site appear more quickly? The answer comes in several parts.
How long does it take for a site to be listed on Google?
Although nothing is guaranteed in the world of search engine listings, and the standard answer is that Google will include your site between a few days and a few weeks, there are steps you can take to make it more likely for your site to appear early. Your domain name and website name will appear first, keywords and content information will take longer.Steps you can take for your site to appear more quickly on Google after launch:
1. Submit your website to Google, Yahoo and Bing.
We will add your website to the search engines. This is the modern way of letting them know you have a new site. It is also an excellent way to find out if Google sees any problem with your site.2. Make sure you have a sitemap, and that it is submitted
A sitemap helps Google understand the structure of your site, what is important and what is new. It is essential that you have one in place, and most content management systems have an automated system to create one for you. For example, if you run your site on WordPress, you can download a free sitemap plugin.3. Make sure your site actually has good content, that is built well and follows good SEO principles
If your site is not contributing anything new or original to the world, then your chances of appearing quickly on Google, or appearing at all are pretty slim, and rightly so. You need to have content that is of some sort of relevance to people, and is structured properly.4. Get some high quality sites to link to you
A little knowledge is a bad thing, and some website owners panic when they don’t get traffic in the first few days after launch and start signing up to shady services that promise to link to them, or exchange links with them. You should not succumb to these temptations, which will have the opposite effect. Instead consider if there are ways to get good quality sites with content that is relevant to your own site’s content to link to you. These links are ‘votes of confidence’ and will tell Google that your site is worthy.5. Have a blog on your site, and update it regularly
Your site appearing on Google is not the endgame. It is only the beginning, and over time your exposure on it will increase. If you don’t want your site to drop off for irrelevance, you need to update it regularly so that it is fresh, and a blog is one good way of making sure you keep it fresh.6. Include different type of content
Google crawls your site and treats different types of content differently. It is possible that blog content will appear at a different time on search results to when images from the site appear on Google image search. It follows that it is a good idea to have different types of content on your site: text, images, video, blog and so on.7. Have a social media presence
If people are talking about you on Twitter or Facebook, this may well improve your chances of appearing faster on Google. At the very least, ensure you have a Google+ page, and Twitter account linking back to your page. Watch out though for spam. You do not want to go out and comment on lots of blogs or try to artificially inflate your site’s followers in social media, as this might have the opposite effect.2Remote Desktop Support Help?
Allow IT WebSmith to access your computer securely over the Internet.
Download the Zoom Client program
Note:
 in your meeting controls, then select one of the following options:
in your meeting controls, then select one of the following options:
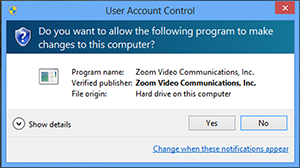
 They may need to accept an additional administrator prompt allowing them access to make changes.
They may need to accept an additional administrator prompt allowing them access to make changes.
 Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
 If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.
If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.

 They will be prompted to choose which application to share.
They will be prompted to choose which application to share.
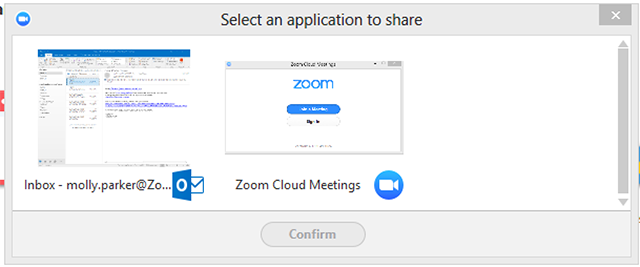
- If the user on the other end is using a Windows, instruct them to Enable the remote control of all applications in their Zoom desktop client settings.
- During a remote support session, the user that requested control can enter admin credentials in UAC (User Access Control) windows if prompted.
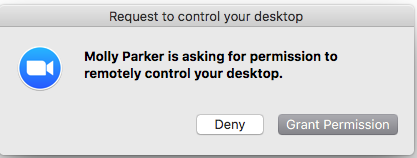
Desktop control
Select Request Desktop Control to prompt the remote user to share their desktop. After the request is made, the remote end will see the following: They may need to accept an additional administrator prompt allowing them access to make changes.
They may need to accept an additional administrator prompt allowing them access to make changes.
 Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
 If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.
If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.

Application control
Select Request Application Control to prompt the remote user to share a specific application. After the request is made, the remote end will see the following: They will be prompted to choose which application to share.
They will be prompted to choose which application to share.

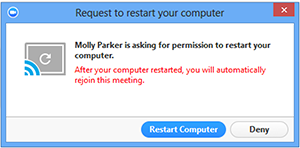
Computer restart
Select Request Computer Restart to prompt the remote user to restart their computer. Once restarted, they will rejoin the Zoom meeting.
Click Support  in your meeting controls, then select one of the following options:
in your meeting controls, then select one of the following options:
 If they have multiple desktops, they will be prompted to select which to share.
If they have multiple desktops, they will be prompted to select which to share.
 Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
 If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.
If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.

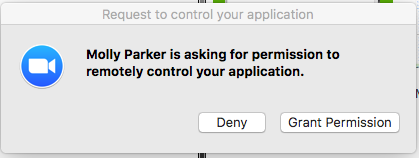 They will be prompted to choose which application to share.
They will be prompted to choose which application to share.


Desktop control
Select Request Desktop Control to prompt the remote user to share their desktop. After the request is made, the remote end will see the following: If they have multiple desktops, they will be prompted to select which to share.
If they have multiple desktops, they will be prompted to select which to share.
 Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
Once the desktop is selected, the host will have remote control of the far ends desktop.
 If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.
If the participant is using multiple screens, you can select which screen you want to control.

Application control
Select Request Application Control to prompt the remote user to share a specific application. After the request is made, the remote end will see the following: They will be prompted to choose which application to share.
They will be prompted to choose which application to share.

Computer restart
Select Request Computer Restart to prompt the remote user to restart their computer. Once restarted, they will rejoin the Zoom meeting.
3How to setup an FTP Solution?
Filezilla
FileZilla, the free FTP solution. Both a client and a server are available. FileZilla is open source software distributed free of charge under the terms of the GNU General Public License.
FTP Solution
4What are my Mail Client Manual Settings?
You can manually configure your mail client using the settings below:
Notes:
| Username: | your@email.com |
| Password: | Use the email account’s password. |
| Incoming Server: | mail.domain.com
|
| Outgoing Server: | mail.domain.com
|
|
IMAP, POP3, and SMTP require authentication. |
|
- IMAP email access coordinates between the server and your mail application. Messages that have been read/deleted/replied to will show up as such, both on the server and in the mail application.
- POP3 does not coordinate with the server. Messages marked as read/deleted/replied to in the mail application will not show up as such on the server. This means that future mail downloads with POP3 will show all messages as unread.
- Outgoing mail is sent using SMTP.
- We recommend using POP3 over SSL/TLS or IMAP over SSL/TLS since they provide increased security for your interactions with the remote mail server.
5What's an SSL?
The most common and well-known use of SSL/TLS is secure web browsing via the HTTPS protocol. A properly configured public HTTPS website includes an SSL/TLS certificate that is signed by a publicly trusted CA. Users visiting an HTTPS website can be assured of:
- Authenticity. The server presenting the certificate is in possession of the private key that matches the public key in the certificate.
- Integrity. Documents signed by the certificate (e.g. web pages) have not been altered in transit by a man in the middle.
- Encryption. Communications between the client and server are encrypted.



 Windows
Windows